Imagine the possibilities! A multilingual website allows you to reach potential customers, business partners, and enthusiasts who might not have found you otherwise. Whether you’re an e-commerce store expanding into new markets or a content-driven website looking to engage with diverse readers, having a multilingual website gives you a competitive edge and opens doors to exciting opportunities on a global scale.
Importance of Multilingual Websites:
- Enhanced User Experience: By offering content in users’ native languages, multilingual websites provide a personalized and inclusive experience, fostering better engagement and understanding. Visitors are more likely to spend time on a website that speaks their language, leading to increased conversions and customer satisfaction.
- Global Reach and Market Penetration: By breaking language barriers, multilingual websites allow businesses to tap into new markets and reach a wider audience. This opens up opportunities for expansion, brand recognition, and revenue growth in diverse regions across the globe.
- Competitive Advantage: In competitive industries, having a multilingual website sets businesses apart from their competitors. It showcases a commitment to understanding and serving the needs of customers from different cultural backgrounds, fostering trust and credibility.
Challenges and Considerations for SEO on Multilingual Websites:
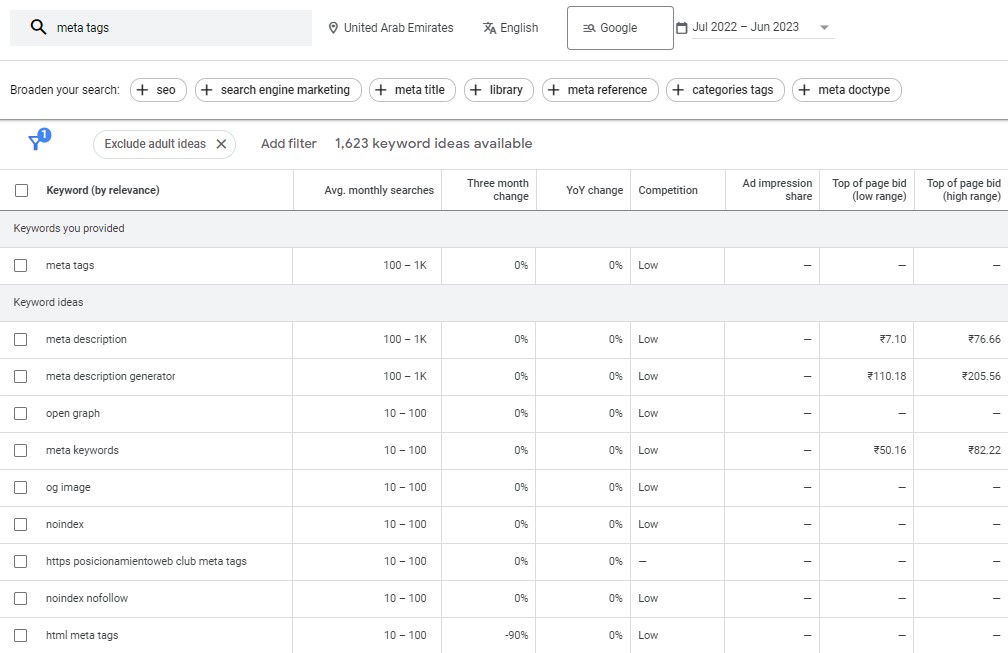
- Keyword Research: Conducting keyword research for each target language is crucial. Language-specific keywords, search patterns, and cultural nuances must be taken into account to optimize content for each language effectively.
- Content Localization: Translating content accurately and contextually is essential. Professional translators or reputable translation services should be employed to maintain high-quality standards and avoid misinterpretation.
- Technical Implementation: Proper URL structure, hreflang tags, and language switchers need to be implemented to indicate language and regional targeting to search engines.
- Maintenance and Updates: Multilingual websites require ongoing maintenance to keep content up-to-date in all languages, monitor for broken links, and adapt to evolving SEO trends and algorithms.
Keyword Research
Identifying Target Languages and Regions:
- Market Analysis: Start by analyzing your target audience and determining the languages spoken in the regions you aim to reach. Consider factors such as customer demographics, market potential, and business objectives.
- Language Preference: Identify the languages preferred by your target audience. This could be based on linguistic data, customer surveys, or website analytics.
- Regional Variations: Understand regional dialects or variations within a language. This knowledge helps you tailor your keyword research for specific regions.
Conducting Keyword Research for Each Target Language:
- Translate Core Keywords: Begin by translating your core keywords into each target language. These primary terms define your products, services, or content.
- Localize Keyword Phrases: Explore localized keyword phrases specific to each target language. Consider regional slang, idiomatic expressions, or commonly used phrases that resonate with the local audience.
- Keyword Research Tools: Leverage keyword research tools like Google Keyword Planner, SEMrush, or Ahrefs to identify relevant keywords in each target language. These tools provide insights into search volume, competition, and related terms.
- Competitor Analysis: Analyze the keywords used by competitors in your target regions. This helps you understand the competitive landscape and discover additional keyword opportunities.
Considering Language-Specific Keywords and Cultural Nuances:
- Language-Specific Keywords: Remember that direct translations may not capture the target language’s true intent or commonly used terms. Consider language-specific keywords that align with local search behavior.
- Cultural Nuances: Take cultural nuances into account when selecting keywords. Certain terms, symbols, or references may have different meanings or cultural sensitivities in different regions. Adapt your keyword choices accordingly.
- Local Search Trends: Stay updated on local search trends and changes in search behavior for each target language. Monitor industry-specific keywords and trending topics to optimize your content accordingly.
- User Intent: Understand the user intent behind keyword searches in each target language. This helps you create relevant and valuable content that aligns with user expectations.
URL Structure
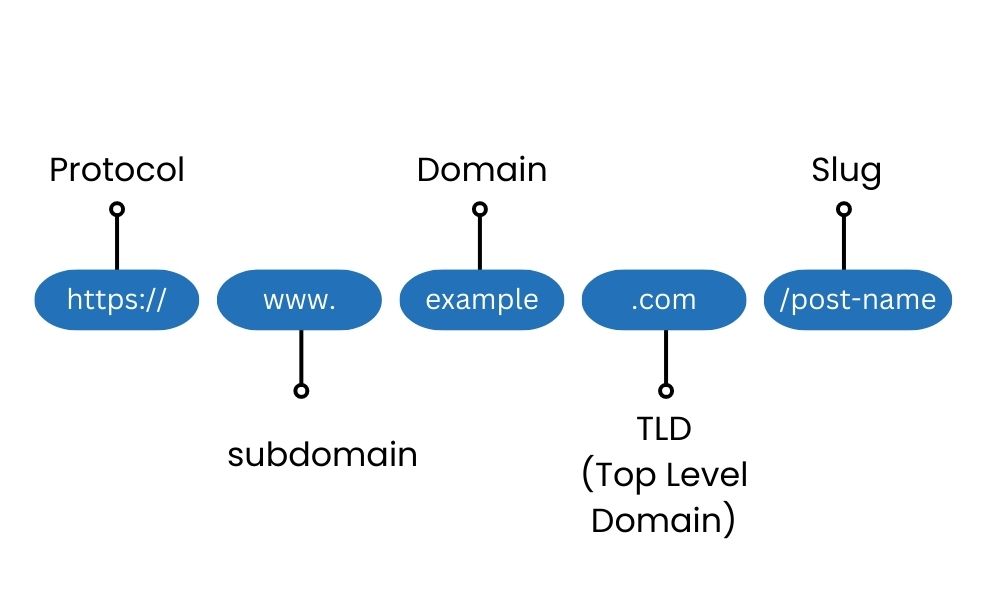
Choosing a URL Structure that Supports Multilingual Content:
- User-Friendly Structure: Opt for a URL structure that is user-friendly and easy to understand across languages. It should convey the language and content of the page intuitively.
- Consistency: Maintain consistency in the structure throughout your website to enhance user experience and make it easier for search engines to crawl and index your pages.
Using Language-Specific Subdirectories or Subdomains:
- Subdirectories (e.g., example.com/for/): Use language-specific subdirectories to organize your content based on languages. For example, ‘fr’ for French, ‘es’ for Spanish, and so on. This approach keeps all language versions under the main domain, improving site structure and localization.
- Subdomains (e.g., for.example.com): Alternatively, utilize language-specific subdomains to separate language versions. This allows for greater flexibility but requires additional maintenance and setup.
- Considerations: When choosing between subdirectories and subdomains, consider factors such as ease of implementation, scalability, localization needs, and the target audience’s preferences.
Implementing Hreflang Tags for Language and Regional Targeting:
- Purpose of Hreflang Tags: hreflang tags help search engines understand your web pages’ language and regional targeting. They indicate the relationship between equivalent content in different languages or regions.
- Implementation: Place hreflang tags in the head section of your HTML code, specifying the language and/or country/region for each version of the page. Ensure the tags accurately reflect the relationship between the different language versions.
- Sitemap Inclusion: Include language-specific URLs with hreflang annotations in your XML sitemap. This helps search engines discover and index the relevant language versions of your content.
- Country-Specific Targeting: If your website targets specific countries or regions, consider combining hreflang tags with country-targeting settings in search engine tools like Google Search Console.
Content Localization
Translating Content Accurately and Contextually:
- Contextual Understanding: When translating content, it’s crucial to understand the context, cultural nuances, and target audience. Translators should have a deep understanding of both the source and target languages to ensure accurate translations.
- Localization vs. Literal Translation: Localization involves adapting content to the target culture, considering idiomatic expressions, cultural references, and preferences. It goes beyond word-for-word translation to provide the audience with a more natural and relevant experience.
- Maintaining Tone and Style: Translated content should retain the original tone and style to maintain brand consistency. This requires linguistic expertise and a thorough understanding of the source material.
Hiring Professional Translators or Using Reputable Translation Services:
- Linguistic Expertise: Professional translators possess linguistic skills, cultural knowledge, and subject matter expertise to convey the intended message in the target language accurately. They can provide high-quality translations that align with your brand’s voice and tone.
- Quality Assurance: Reputable translation services often have quality assurance processes in place, ensuring accurate and reliable translations. They may offer proofreading, editing, and revision services to ensure the highest standards of quality.
- Specialization: Consider hiring translators with expertise in your industry or domain. This ensures accurate terminology usage and a better understanding of the subject matter.
Avoiding Machine Translation for High-Quality Results:
- Limitations of Machine Translation: Machine translation, such as automated tools or AI-based systems, can be useful for basic understanding but often lack accuracy, contextual understanding, and cultural adaptation. They may produce literal translations that sound unnatural or misleading.
- Potential Errors and Misinterpretations: Machine translation algorithms may not capture the complexity of language or cultural nuances, leading to errors, misinterpretations, and potential misunderstandings for the audience.
- Reputation and User Experience: Low-quality translations can negatively impact your brand’s reputation and user experience. Users may perceive inaccurately translated content as unprofessional or unreliable.
Metadata Optimization
Translating Meta Tags for Each Language:
- Title Tags and Meta Descriptions: Translate title tags and meta descriptions accurately to reflect the content of each page in the target language. This ensures that users and search engines understand the purpose and relevance of the page.
- Cultural Context: Consider cultural nuances and preferences when translating meta tags. Certain phrases or idioms may require adaptation to resonate effectively with the target audience.
Optimizing Meta Tags for Relevant Keywords and User Intent:
- Keyword Research: Conduct keyword research for each target language to identify relevant terms and phrases. Incorporate these keywords naturally into the translated meta tags while keeping the user intent in mind.
- Search Intent Alignment: Ensure that the meta tags align with the user’s search intent for each language. Craft them in a way that captures the essence of the page’s content and encourages users to click through.
- Localization: Adapt meta tags to suit the preferences and search behavior of the target audience in each language. This includes considering regional variations and localized search terms.
Using Unique and Compelling Meta Tags for Each Language Version:
- Uniqueness: Create unique meta tags for each language version of a page. Avoid duplicating meta tags across different language versions, as this can lead to confusion and suboptimal search engine optimization.
- Compelling Content: Craft meta tags that are compelling and enticing to users in each language. Use persuasive language, calls-to-action, and unique selling points to capture attention and encourage clicks.
- Localization and Cultural Relevance: Tailor the messaging in meta tags to be culturally relevant and resonate with the target audience in each language. This helps create a personalized experience and improves click-through rates.
On-Page Optimization

Translating and Optimizing Headings, Image Alt Tags, and Anchor Texts:
- Headings: Translate and optimize headings (H1, H2, etc.) to accurately reflect the content of each page in the target language. Incorporate relevant keywords naturally while maintaining clarity and coherence.
- Image Alt Tags: Translate image alt tags to provide accurate descriptions of images in the target language. Optimize alt tags by including relevant keywords when appropriate while ensuring they remain descriptive and informative.
- Anchor Texts: Translate and optimize anchor texts of internal and external links to provide clear and relevant context for users and search engines. Use descriptive anchor texts that accurately represent the linked content.
Ensuring Proper Formatting and Structure in Translated Content:
- Consistent HTML Structure: Ensure that the HTML structure of translated content mirrors that of the original content. This includes maintaining proper use of header tags, paragraphs, lists, and other formatting elements.
- Language-Dependent Formatting: Adapt formatting elements, such as date formats, currency symbols, or quotation styles, to align with the conventions of the target language and locale.
- Readability and Accessibility: Pay attention to the readability and accessibility of translated content. Use clear, concise sentences, bullet points, and appropriate spacing to enhance comprehension and user experience.
Maintaining Consistency in Website Design and User Experience across Languages:
- Design Elements: Maintain consistent design elements, such as logos, color schemes, and typography, across all language versions of your website. This ensures a cohesive brand experience and helps users navigate seamlessly.
- Navigation and User Interface: Keep the navigation structure and user interface consistent across languages, making it easy for users to switch between language versions without confusion. Maintain consistent labeling and placement of navigation elements.
- User Experience Optimization: Optimize user experience by considering each target audience’s preferences and cultural nuances. Adapt content and features to suit users’ expectations and browsing habits in different languages.
Regular Updates and Maintenance

Keeping Content Up-to-Date in All Languages:
- Content Review and Refresh: Regularly review and update content across all language versions of your website. Ensure that information, product details, and relevant resources are accurate, current, and aligned with the latest developments in your industry.
- Localized Updates: Pay attention to region-specific updates, cultural events, or holidays that may impact your target audience. Adapt and update content accordingly to maintain relevance and resonate with users in each language.
- Multilingual Content Creation: Continuously add fresh and valuable content in each language to attract and engage users. Consider creating localized blog posts, news articles, or resources that cater specifically to the interests and needs of each target audience.
Monitoring for Broken Links and Fixing Them Promptly:
- Regular Link Audits: Conduct periodic link audits to identify broken links or redirects across all language versions of your website. Use tools or website crawlers to scan and detect any issues.
- Prompt Resolution: When broken links are detected, promptly fix or redirect them to relevant and working pages. This ensures a seamless user experience and helps maintain a positive impression of your website.
- User-Friendly Error Pages: Customize error pages in each language to guide users back to relevant content or provide helpful suggestions. Offer clear navigation options or search functionality to assist users in finding the information they were seeking.
Continuously Improving SEO Strategies Based on Evolving Trends and Algorithms:
- Stay Updated with SEO Trends: Keep abreast of the latest SEO trends, algorithm updates, and best practices in the industry. Stay connected with reliable sources, attend conferences, and follow reputable SEO blogs to remain informed.
- Regular SEO Audits: Conduct periodic SEO audits for each language version to identify areas for improvement. Evaluate keyword targeting, on-page optimization, and technical aspects such as website speed, mobile-friendliness, and structured data.
- Adaptation to Algorithm Changes: Adjust your SEO strategies and tactics based on algorithm updates from search engines. Monitor the impact of algorithm changes on search rankings and user engagement metrics, and make necessary adjustments to maintain visibility and performance.
Conclusion
Optimizing a multilingual website for SEO requires careful attention to language-specific keywords, localized content, and user experience. You can maximize your website’s visibility, reach, and organic traffic by implementing effective SEO strategies, such as conducting thorough keyword research, providing accurate translations or adaptations, and ensuring a consistent user experience across different language versions.
If you need assistance with creating and optimizing a multilingual website, Techies Infotech is here to help. Our team of experts specializes in multilingual website development and SEO services. Contact us today to learn more about how we can enhance your online presence and provide customized solutions for your multilingual website needs.
Remember, with Techies Infotech, you can take your multilingual website to new heights and effectively connect with a global audience.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. What are the benefits of having a multilingual website?
- Expanded reach to a larger audience who prefer browsing in their native language.
- Enhanced user experience due to vernacular content.
- Increased credibility and trust.
- Enhanced SEO and organic traffic from language-specific search queries.
- Competitive advantage in multilingual markets.
Q. How do I create my website’s multi-language copy?
- Identify target languages based on your audience and market.
- Hire professional translators or localization experts to translate or adapt your content accurately.
- Implement language switch functionality for easy language selection.
- Ensure a consistent user experience across all language versions.
Q. What types of keywords should I target for my multilingual website?
- Language-specific keywords reflect the search behavior in each target language.
- Localized keywords to target users in specific regions or countries.
- Consider cultural differences, idiomatic expressions, and colloquial terms in each language.
- Conduct keyword research using language-specific keyword research tools for popular and relevant keywords.